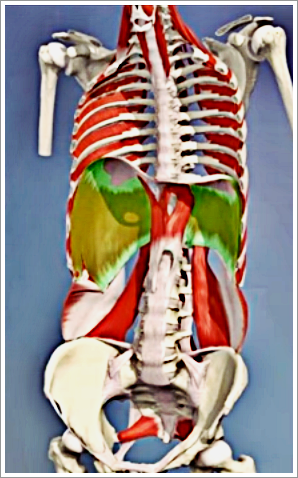
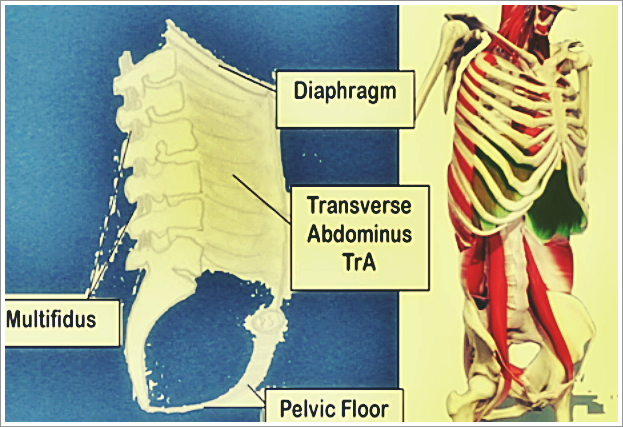
The diaphragm is the mushroom shaped muscle present between the two most important cavities in the body, i.e., the thorax and the abdomen. It is located between the under the middle and lower rib cage. It is considered as one of the vital muscles of the body due to the role that it plays in the process of respiration. It facilitates the process of breathing by helping the lungs rise and expand and by reducing the overall pressure exerted on the lungs.
Diaphragm pain can occur due to a variety of different reasons. It may be observed in patients who have undergone cardiac surgery; it may occur as a symptom of different underlying illnesses; it may occur due to an inefficient pattern of respiration; or the causes may be unknown.
Treatment of diaphragm pain is dependent on proper diagnosis and treatment of the underlying cause.
Symptoms
Some of the common signs and symptoms of diaphragm pain are as follows:
- Pain may be felt in the chest area
- The middle section of the back may experience pain in a band-like formation
- Pain may occur around the ribs
- Stinging or sharp pain on the sides of the chest is another possible symptom
The above symptoms are often experienced when engaged in sporty activities when the person is gasping for breath. People with asthma, bronchitis, pneumonia, or emphysema may also experience such form of diaphragm pain.
Causes of Diaphragm pain
Some of the common causes of diaphragm pain are mentioned below:
- Innervation problems: Pain in diaphragm may be caused due to innervations defects such as:
- Neuropathic abnormalities in phrenic nerves caused due to injuries that may occur during surgeries or growth on tumors on them may cause diaphragm muscle pain. It may be noted that the phrenic nerves send signals for innervation of the diaphragm.
- Any instances of a stroke which results in paralysis of one side of the diaphragm muscle results in excess workload on the other side, which may then trigger diaphragm pain.
- Innervation issues caused due to underlying ‘myasthenia gravis’ disease which hampers breathing capacity is another cause.
- Any kind of spinal cord disease can also lead to pain in the diaphragm
- Anatomical problems: Pain in diaphragm may occur due to anatomical defects like:
- Defect in the muscle which is congenital or present from birth
- Acquired defects which may occur as a side effect of injuries, traumas, or post-operation situations
- Pre-existing diseases: People with certain diseases may suffer from diaphragm pain as a symptom of that underlying disease. These conditions can be:
- Hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism
- Multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/ALS, poliomyelitis, or other neurological conditions
- Rheumatoid arthritis or other disorders that affect the connective tissue
- Muscle disorders like muscular dystrophy which affects the diaphragm muscle
- Costochondritis, pleurisy, splenic disease, pancreatitis, and gallbladder ailments
- Other conditions: In some cases, pain in diaphragm may arise due to conditions like
- Injury or trauma to the ribcage; rupture diaphragm muscle due to trauma to the chest; lower ribcage fracture
- Infection, chiropractic manipulation, or malnutrition
- Hiatal hernia is a condition where the stomach protrudes and stretches the diaphragm muscle. People who eat excessive are at a greater risk to suffering from hiatal hernia.
- Sprain, increased strain, or tear in other internal organs located in the cavities of the body.
- Non-serious causes: Diaphragm pain can be considered to be normal and not a sign of trouble in the following cases:
- Women may experience breathless and well as pain in diaphragm during pregnancy. This is due to expansion of the uterus to make space for the growing fetus in the abdomen. The expansion of the uterus exerts pressure in the diaphragm causing pain.
- People with a chronic cough due to smoking, etc. or excessive coughing by patients of cold or flu may suffer from diaphragm pain as coughing produces increased pressure on the muscle.
- Running often tends to increase the rate of breathing and the overall use of the muscles. Hence, it is recommended for people to warm up before running so as to increase the breathing capacity. People who do not warm up before running may experience diaphragm pain. This is due to the fact that the diaphragm contracts to its limit to keep up with the pace of breathing, thereby increasing the pressure on the muscle and resulting in pain.
Diaphragm Pain – Remedies
Treatment of diaphragm involves diagnosis of the underlying cause and then treating it as per standard medical procedures. A few treatment options are listed below.
Doctors may prescribe different medications for the following conditions:
- Neurologic medicines are used for treating spinal cord problems
- Treatment of pain caused by a stroke involves use of heart medications so as to prevent occurrence of stroke and alleviate pain
- Morphine is prescribed for extreme pain caused by diaphragm rupture
- Anti-inflammatory drugs are given for rheumatoid arthritis; in case of severe pain, doctors may go for corticosteroids
Surgery is recommended in following cases of pain in diaphragm:
- In case of phrenic nerve problems doctors may place a phrenic nerve pacemaker in the muscle to assist the nerves for breathing.
- Surgery can help correct anatomical defects and thus ease the pain
- Different injuries, trauma, etc. to the muscle as well as hiatal hernia can be treated via surgery
Treatments for other causes of diaphragm pain are:
- Malnutrition treatment involves intake of a health and balanced diet
- Oxygen therapy can help ease diaphragm pain in myasthenia gravis patients
- Eating in a slow manner and proper chewing can help prevent the habit of overeating
- People with neurological conditions who experience diaphragm pain as well as problems in carrying out everyday activities are recommended occupational therapy
- Physical therapy can be very helpful for patients who are suffering from mobility problems for even simple activities like getting out of bed, walking, etc.
- Thyroid problems can be treated with hormone therapy and medications